Reversing Habitat Loss: Strategies for Restoring Biodiversity
Habitat loss is one of the primary drivers of biodiversity decline worldwide. The loss and fragmentation of natural habitats pose significant threats to countless plant and animal species. However, there is hope in reversing habitat loss and restoring biodiversity through dedicated conservation efforts. In this blog, we will explore strategies for restoring habitats and rejuvenating biodiversity.
Habitat Restoration:
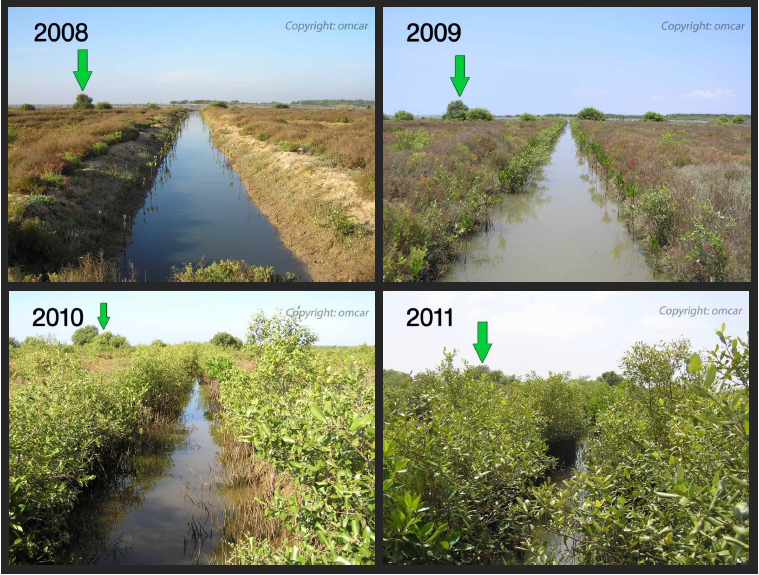
Habitat restoration involves the active rehabilitation and reconstruction of degraded or destroyed habitats. This can include reestablishing native vegetation, restoring water bodies, and reintroducing key species. By recreating suitable habitats, we provide refuge and resources for a diverse range of species, allowing populations to recover and thrive.
Conservation Landscapes:
Creating conservation landscapes involves connecting fragmented habitats through corridors or protected areas. These landscapes provide migratory pathways for wildlife, facilitate genetic exchange, and enhance species movement. Conserving and restoring large, contiguous habitats are vital for maintaining ecological processes and supporting diverse populations.
Rewilding Initiatives:
Rewilding aims to reintroduce key species and restore natural ecological processes in degraded areas. By reintroducing predators, herbivores, and keystone species, we can recreate balanced ecosystems. Rewilding efforts can help control populations of certain species, restore natural grazing patterns, and promote biodiversity through ecological cascades.
Invasive Species Management:
Invasive species pose a significant threat to native biodiversity. Managing and controlling invasive species is crucial for restoring habitats. This can involve measures such as targeted removal, habitat modification, and the introduction of biological controls. By reducing the impact of invasive species, we create opportunities for native species to thrive.
Community Engagement and Conservation Education:
Engaging local communities and raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity conservation is vital for long-term success. Encouraging sustainable land-use practices, supporting community-led conservation initiatives, and promoting environmental education foster a sense of stewardship and ensure the continued protection of restored habitats.
Collaboration and Policy Support:
Successful habitat restoration and biodiversity conservation require collaboration between government agencies, non-profit organizations, local communities, and scientific institutions. Developing and implementing policies that prioritize habitat restoration, protected area expansion, and sustainable land-use planning is crucial for creating an enabling environment for restoration efforts.
Conclusion:
Reversing habitat loss and restoring biodiversity is a challenging but crucial task. Through habitat restoration, conservation landscapes, rewilding initiatives, invasive species management, community engagement, and policy support, we can restore habitats and promote the recovery of biodiversity. These strategies must be implemented on local, regional, and global scales to ensure the long-term preservation of ecosystems and the species that depend on them. By working together, we can create a more sustainable future where biodiversity thrives, benefiting both nature and humanity.
Good strategies
ReplyDelete